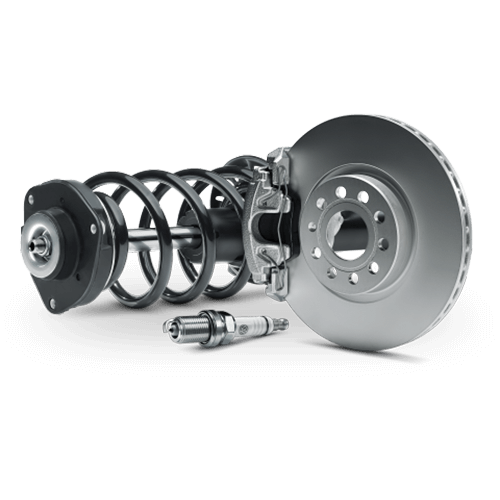
What is the function of the caliper in the car brake
Every component in the intricate world of automotive engineering plays a critical role in ensuring a vehicle's safety and functionality. The brake caliper is one such component that often goes unnoticed but is critical to the smooth operation of a car's braking system. In this article from the Bestparts website, we delve into the depths of automotive mechanics to uncover the mysteries behind the caliper and explore its pivotal function in car brake systems.
How does a brake caliper work in a car?
A brake caliper in a car is essential to the braking system because it converts hydraulic pressure into mechanical force. Here's a step-by-step explanation of how a brake caliper works:
- Hydraulic Pressure Generation
When the driver applies the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure is generated in the master cylinder of the brake system.
- Transmission of Hydraulic Pressure
This hydraulic pressure is transmitted through brake fluid-filled lines to the brake calipers located at each wheel.
- Piston Activation
Within the brake caliper, there are pistons that are activated by the hydraulic pressure. The number of pistons can vary depending on the type of caliper (floating or fixed).
- Brake Pad Compression
The activated pistons push against the brake pads. In a floating caliper, the piston moves on a sliding mechanism to press against one side of the rotor, while in a fixed caliper, pistons on both sides of the rotor are engaged.
- Friction Generation
The brake pads, now in contact with the rotor, create friction. This friction is what slows down or halts the rotation of the wheels.
- Conversion of Kinetic Energy to Heat
As the wheels slow down, the kinetic energy is converted into heat due to the friction between the brake pads and the rotor.
- Heat Dissipation
Calipers are designed with features to efficiently dissipate the heat generated during braking. This prevents overheating and ensures consistent braking performance.
- Release of Pressure
When the driver releases the brake pedal, the hydraulic pressure in the caliper is released. This retracts the pistons and allows the wheel to rotate freely again.
- Even Brake Pad Wear
Calipers play a crucial role in ensuring even brake pad wear by exerting uniform pressure on both sides of the rotor. This contributes to the longevity and optimal performance of the braking system.
In summary, the brake caliper is a vital component that translates the driver's input into the mechanical action needed to slow down or stop the vehicle. Its precise functioning is essential for both safety and the overall performance of the car's braking system.

The difference between a floating caliper and a sliding brake caliper
The terms "floating caliper" and "sliding caliper" are often used interchangeably, causing some confusion. However, in the context of automotive braking systems, these terms can refer to different designs. Let's explore the key differences between a floating caliper and a sliding caliper:
Floating Caliper
Design
- A floating caliper has a single piston located on one side of the caliper.
- The caliper is designed to move laterally or "float" on guide pins or bolts.
Operation
When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic pressure activates the piston.
- The caliper slides on the guide pins, causing the piston to press against one side of the brake rotor.
- This movement creates friction between the brake pads and the rotor, slowing down the wheel.
Common Usage
Floating calipers are commonly found in everyday vehicles, providing a cost-effective and simple design for standard braking needs.
Sliding Caliper
Design
- A sliding caliper, in contrast, typically has two pistons on opposite sides of the caliper.
- The caliper itself remains stationary and does not slide laterally.
Operation
- When hydraulic pressure is applied, both pistons are activated simultaneously.
- The pistons press against either side of the brake rotor, creating friction and slowing down the wheel.
Common Usage
- Sliding calipers are often associated with older brake system designs and may not be as prevalent in modern vehicles.
- They can still be found in certain applications, especially in rear brake systems.

Advantages and Disadvantages
Floating Caliper Advantages:
- Simplicity of design
- Cost-effective to manufacture
- Lighter weight
Floating Caliper Disadvantages:
- May not provide as much braking force as fixed calipers
- Can be prone to uneven pad wear
Sliding Caliper Advantages:
- Can provide more even pressure distribution on both sides of the rotor.
- May offer better braking performance in certain conditions.
Sliding Caliper Disadvantages:
- Typically heavier and more complex than floating calipers.
- Potentially higher manufacturing costs.
In overall, while the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, a floating caliper denotes lateral movement, whereas a sliding caliper denotes individual piston movement. The choice between them depends on the specific design requirements and performance characteristics desired for a particular vehicle's braking system.
How does a Floating Caliper Work?
A floating caliper operates by utilizing a single piston or set of pistons on one side of the caliper. Unlike a fixed caliper that has pistons on both sides, the floating caliper is designed to "float" or slide laterally on pins or guide bolts. This design allows the caliper to move slightly during the braking process.
When the driver applies the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure is generated in the master cylinder. This pressure is transmitted through brake lines to the caliper. In a floating caliper system, the hydraulic pressure pushes the caliper to slide on its mounting pins or bolts. As the caliper moves, it brings one of the brake pads into contact with the rotor.

The function of caliper brake causes it to pivot, and this action then forces the other brake pad to make contact with the opposite side of the rotor. The resulting friction between the brake pads and the rotor slows down the wheel's rotation, facilitating the braking process.
The key characteristic of a floating caliper is its ability to slide or float laterally to apply pressure on one side of the rotor, inducing a pivoting motion that brings the opposite brake pad into contact with the other side of the rotor. This design allows for a simpler and more cost-effective braking system compared to some other caliper designs.
Signs of Car Brake Caliper Failure
Recognizing signs of car brake caliper failure is crucial for maintaining a safe and functional braking system. Here are key indicators that may suggest issues with your brake calipers:
Uneven Brake Pad Wear
Uneven wear on the brake pads, where one pad appears significantly more worn than the other, can signal problems with the caliper's ability to apply consistent pressure.
Vehicle Pulling to One Side
If your car pulls to one side when braking, it could indicate uneven braking force, possibly caused by a sticking or malfunctioning caliper on one side.
Squeaking or Grinding Noises
Unusual noises during braking, such as squeaks or grinds, may be attributed to caliper issues. This could result from uneven pressure application or worn-out brake pads.
Leaking Brake Fluid
Brake fluid leaks around the caliper could indicate damaged seals or a fluid leak from the caliper itself. Any brake fluid leakage requires immediate attention.
Reduced Braking Performance
A noticeable decrease in braking efficiency, longer stopping distances, or a spongy brake pedal may suggest caliper problems affecting the proper functioning of the braking system.

Hot or Overheated Brakes
Overheated brakes, indicated by a burning smell or smoke, can be a sign of a caliper that is not releasing properly, leading to continuous friction and heat buildup.
Visible Damage or Corrosion
Inspect the calipers for visible damage, such as cracks or severe corrosion. Damaged calipers may compromise their structural integrity and functionality.
Warning Light Activation
Modern vehicles are equipped with brake warning lights. If the brake warning light on the dashboard illuminates, it could signal issues with the brake system, including the calipers.
Brake Dragging Sensation
If you feel a dragging sensation while driving, it may indicate that one or more calipers are not releasing properly, causing continuous contact between the brake pads and the rotor.
Vibration During Braking
Excessive vibration or pulsation through the brake pedal while braking may suggest uneven brake pad contact caused by caliper irregularities.
If any of these signs are observed, it is advisable to have the brake system inspected promptly by a qualified mechanic. Timely intervention can prevent further damage, ensure optimal braking performance, and contribute to overall road safety.
What Happens When a Caliper Takes its Final Bow?
When the caliper fails to perform, the consequences can be dire. Braking efficiency plummets, wear on brake components becomes erratic, and in extreme cases, the entire brake system may stage a silent mutiny. This is not merely a mechanical glitch; it's a safety concern demanding immediate attention.

Painting Your Brake Caliper: A Step-by-Step Guide
When it comes to enhancing the aesthetic appeal of your vehicle and adding a touch of personalization, painting the brake calipers is a popular and relatively simple DIY project. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you achieve a professional-looking finish on your brake calipers.
Gather Your Materials
Before diving into the painting process, make sure you have the following materials on hand:
- High-temperature brake caliper paint
- Brake cleaner
- Masking tape
- Brushes or spray gun
- Sandpaper or abrasive pad
- Jack and jack stands
Lift and secure the vehicle to access the calipers safely.
Step 1: Lift and Secure the Vehicle
- Safely lift the vehicle using a jack and secure it with jack stands.
- Ensure the vehicle is on a stable and level surface before starting the painting process.
Step 2: Remove the Wheels
Loosen the lug nuts, lift the vehicle further, and remove the wheels to access the brake calipers easily.
Step 3: Clean the Calipers
- Use brake cleaner to thoroughly clean the calipers, removing any dirt, grease, or brake dust.
- Ensure the calipers are completely dry before proceeding.
Step 4: Masking
- Use masking tape to cover areas you don't want to paint, such as brake lines, bleeder valves, and other adjacent components.
- This step ensures a neat and precise paint job.
Step 5: Surface Preparation
- Lightly sand the caliper surface using fine-grit sandpaper or an abrasive pad.
- This step promotes paint adhesion and helps create a smooth finish.
Step 6: Apply the Paint
- Follow the instructions on the brake caliper paint for the best results.
- Use a brush or spray gun to apply thin, even coats of paint.
- Allow each coat to dry thoroughly before applying the next.
Step 7: Multiple Coats
- Apply multiple coats to achieve the desired color depth and coverage.
- Be patient and allow sufficient drying time between coats.
Step 8: Final Touches
- Once the final coat is dry, carefully remove the masking tape.
- Reinstall the wheels and lower the vehicle.
Step 9: Cure the Paint
- Follow the paint manufacturer's recommendations for curing time.
- Some paints may require baking, while others may cure naturally.
Step 10: Test Drive
Before hitting the road, perform a gentle test drive to ensure that the paint adheres well and does not exhibit any issues.
By following these steps, you can give your brake calipers a fresh and customized look while maintaining the functionality of your braking system. Remember to choose high-quality paint designed for high-temperature applications to ensure durability and longevity.

How can the braking performance of the car be improved?
Improving the braking performance of a car involves several considerations and potential upgrades. Here are ways to enhance your vehicle's braking efficiency:
Upgrade Brake Pads
High-performance brake pads, designed for better heat dissipation and friction, can significantly improve braking responsiveness. Choose pads that match your driving style and the demands of your vehicle.
Install Performance Rotors
Upgrading to slotted or drilled brake rotors can enhance cooling and reduce brake fade. Performance rotors can handle higher temperatures more effectively, providing improved braking under demanding conditions.
Use Quality Brake Fluid
High-performance brake fluid with a higher boiling point can withstand elevated temperatures, reducing the risk of brake fade. Regularly flushing and replacing brake fluid is essential for maintaining optimal performance.
Consider Brake Caliper Upgrades
Upgrading to larger or high-performance brake calipers can enhance stopping power. Performance calipers are designed for improved clamping force and heat dissipation.
Opt for Stainless Steel Brake Lines
Stainless steel brake lines are more resistant to expansion under pressure compared to rubber lines. This upgrade can result in a firmer brake pedal feel and more responsive braking.
Adjust Brake Bias
Ensuring the appropriate brake bias between the front and rear of the vehicle is crucial for balanced braking. Adjustments may be necessary if modifications are made to the braking system or if the vehicle's weight distribution changes.

Upgrade Brake Master Cylinder
A high-performance master cylinder can provide better brake pedal feel and modulation. Consider upgrading to a master cylinder that matches the braking demands of your vehicle.
Improve Brake Cooling
Enhance brake cooling by installing ducts or shields to direct airflow to the brake components. Excessive heat can lead to brake fade, and improved cooling can mitigate this effect.
Optimize Tire and Wheel Combination
The choice of tires and wheels can impact braking performance. Upgrading to high-performance tires with good grip and a wheel size that accommodates larger brake components can contribute to better braking.
Invest in Performance Brake Kits
Performance brake kits often include upgraded components, such as rotors, pads, and calipers, designed to work together for improved braking performance. These kits are engineered to handle increased demands.
Upgrade Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
If applicable, upgrading or optimizing the ABS system can enhance its effectiveness in preventing wheel lock-up during hard braking, improving overall stability.
Before making any modifications, it's crucial to research and ensure that the chosen upgrades are compatible with your vehicle. Consult with professionals or specialists to get recommendations tailored to your specific driving needs and vehicle type.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the brake caliper is the unsung hero in the realm of automotive safety. Its intricate design and precise functionality ensure that your vehicle responds promptly and effectively to your commands, promoting a secure driving experience.
Whether you're navigating busy city streets or cruising down the open highway, the caliper quietly performs its duty, reminding us that safety is not just a feature—it's a well-engineered masterpiece.
FAQ
- How often should I check my brake calipers?
Regular inspections, akin to tuning a musical instrument, should be part of routine vehicle maintenance. Any signs of caliper trouble warrant immediate attention.
- Can I drive with a failing brake caliper?
Imagine a conductor without a baton; driving with a failing caliper is strongly discouraged due to compromised braking capabilities, endangering both the driver and others on the road.
- What causes uneven brake pad wear?
Uneven brake pad wear often points to issues within the caliper, such as sticking pistons or malfunctioning slide pins, or it may indicate irregularities in the rotor surface.
- Are there performance benefits to upgrading brake components?
Indeed, upgrading to high-performance brake pads, quality rotors, and using superior brake fluid can elevate your vehicle's braking performance, especially in demanding situations.